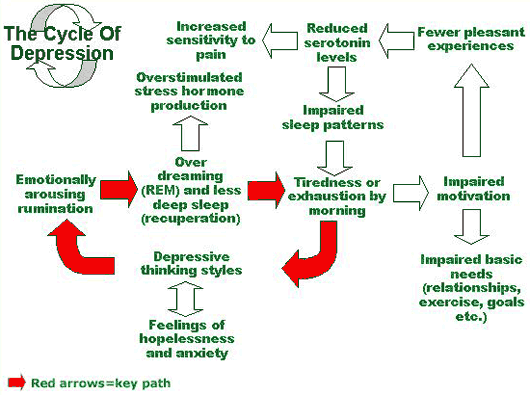
One in five people will experience depression at some time in their life. The cycle of depression can be treated with changing patterns and therapy.
What is a depressive disorder?
They are a group of illnesses characterized excessive or long-term depressed mood and loss of interest in activities that used to be enjoyable. One
in five people will experience depressive disorder at some time during their lives.

- Post-Partum depression Mothers with this illness find it increasingly difficult to cope with the demands of everyday life. They experience anxiety, fear, despondency, sadness and extreme tiredness. Some have panic attacks or become tense and irritable. There may be a change in appetite and sleep patterns.
- Adjustment disorder with depressed mood People with this illness are reacting to a distressing situation in their life, such as, failure of close relationship or loss of a job, but to a degree than its usual. The feelings are very intense and often include anxiety, poor sleep and appetite changes. The symptoms may vary from weeks to years.
- Major depressive disorder A person with major depressive disorder becomes low spirited and loses their enjoyment of life. They lack concentration and energy and have changes in their appetite and sleep patterns. Feelings of guilt, hopelessness and despair can lead to thoughts of suicide. It can be triggered by a distressing event that the person is unable to deal with. When symptoms of are few and mild and last longer the illness is called dysthymic disorder.
- Bipolar mood disorder A person with bipolar mood disorder experiences depressive episodes alternating with periods of mania involving elation, over activity, irritability, rapid speech, and recklessness. In serious instances the person can also have delusions.
- Co-occurring mental health problems People with depression very often experience symptoms of anxiety, harmful alcohol and other drug use. This makes treatment complex. Effectively managing alcohol and other drug use is important. Risk of suicide is heightened.
What causes depressive disorders?
- Genetic factors
Tendency to develop depression runs in families similar to a predisposition to other illness, such as diabetes or heart disease.
- Biochemical factors
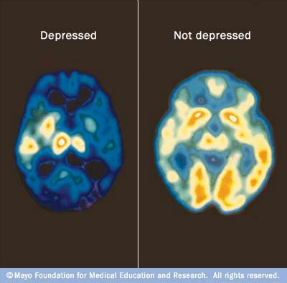
Depressive disorders are thought to be due, in part, to a chemical imbalance in the brain. Anti-depressant medication treats the imbalance.
- Stress
Depressive disorders are more common at certain stages of life that involve major life transitions, such as childbirth, menopause, and bereavement. It is more common in young adults, women, older adults, and people with physical health problems.
- Temperament
People who are perfectionists and self-critical, and who set high standards for themselves and others, are vulnerable to depression. Those who are dependent on other people are susceptible to depression if they are let down.
- Alcohol and other drug use
Alcohol and other drug use make people highly susceptible to depression. This also contributes to high risk of over dose or suicide for people with depressive disorders.
- Environmental factors
Continuous exposure to violence, neglect, abuse or poverty may make people who are already susceptible to depression all the more vulnerable to the illness.
What treatment is available?
Psychological interventions such as Cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) are aimed at changing patterns of thinking, behaviors and beliefs that are related to depression. CBT teaches you how to replace negative unproductive thought patterns with more realistic and useful ones. Interpersonal therapy (IPT), acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) are also effective types of therapy along with family therapy and relaxation techniques. Medications are used to treat chemical imbalances in the brain.
Please CONTACT ME for a consultation and take charge of your Health and Wellness in Mind, Body and Spirit.